| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The trachea branches into the right and left primary bronchi at the carina. These bronchi are also lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium containing mucus-producing goblet cells ( [link] b ). The carina is a raised structure that contains specialized nervous tissue that induces violent coughing if a foreign body, such as food, is present. Rings of cartilage, similar to those of the trachea, support the structure of the bronchi and prevent their collapse. The primary bronchi enter the lungs at the hilum, a concave region where blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves also enter the lungs. The bronchi continue to branch into bronchial a tree. A bronchial tree (or respiratory tree) is the collective term used for these multiple-branched bronchi. The main function of the bronchi, like other conducting zone structures, is to provide a passageway for air to move into and out of each lung. In addition, the mucous membrane traps debris and pathogens.
A bronchiole branches from the tertiary bronchi. Bronchioles, which are about 1 mm in diameter, further branch until they become the tiny terminal bronchioles, which lead to the structures of gas exchange. There are more than 1000 terminal bronchioles in each lung. The muscular walls of the bronchioles do not contain cartilage like those of the bronchi. This muscular wall can change the size of the tubing to increase or decrease airflow through the tube.
In contrast to the conducting zone, the respiratory zone includes structures that are directly involved in gas exchange. The respiratory zone begins where the terminal bronchioles join a respiratory bronchiole , the smallest type of bronchiole ( [link] ), which then leads to an alveolar duct, opening into a cluster of alveoli.
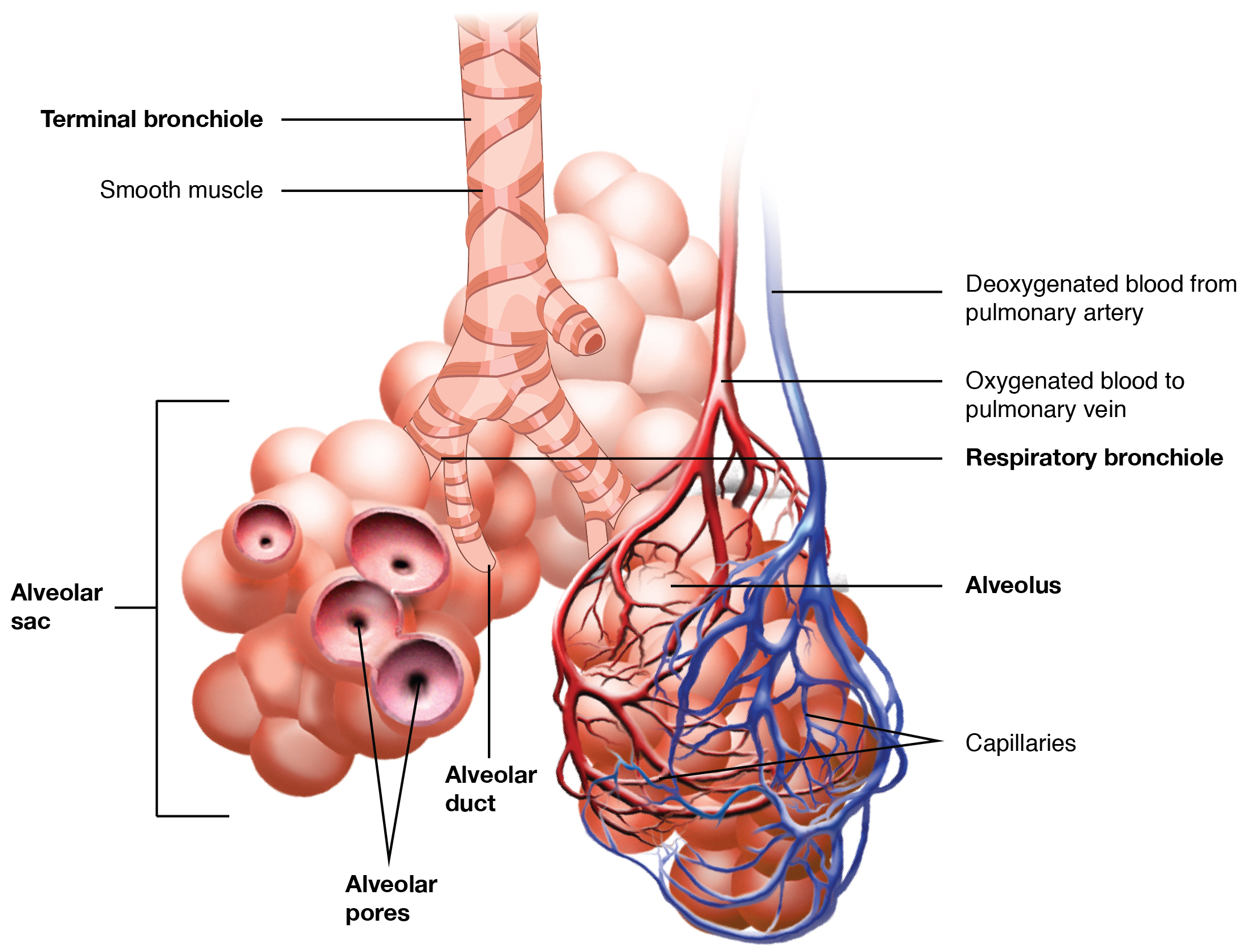
An alveolar duct is a tube composed of smooth muscle and connective tissue, which opens into a cluster of alveoli. An alveolus is one of the many small, grape-like sacs that are attached to the alveolar ducts.
An alveolar sac is a cluster of many individual alveoli that are responsible for gas exchange. An alveolus is approximately 200 μm in diameter with elastic walls that allow the alveolus to stretch during air intake, which greatly increases the surface area available for gas exchange. Alveoli are connected to their neighbors by alveolar pores , which help maintain equal air pressure throughout the alveoli and lung ( [link] ).
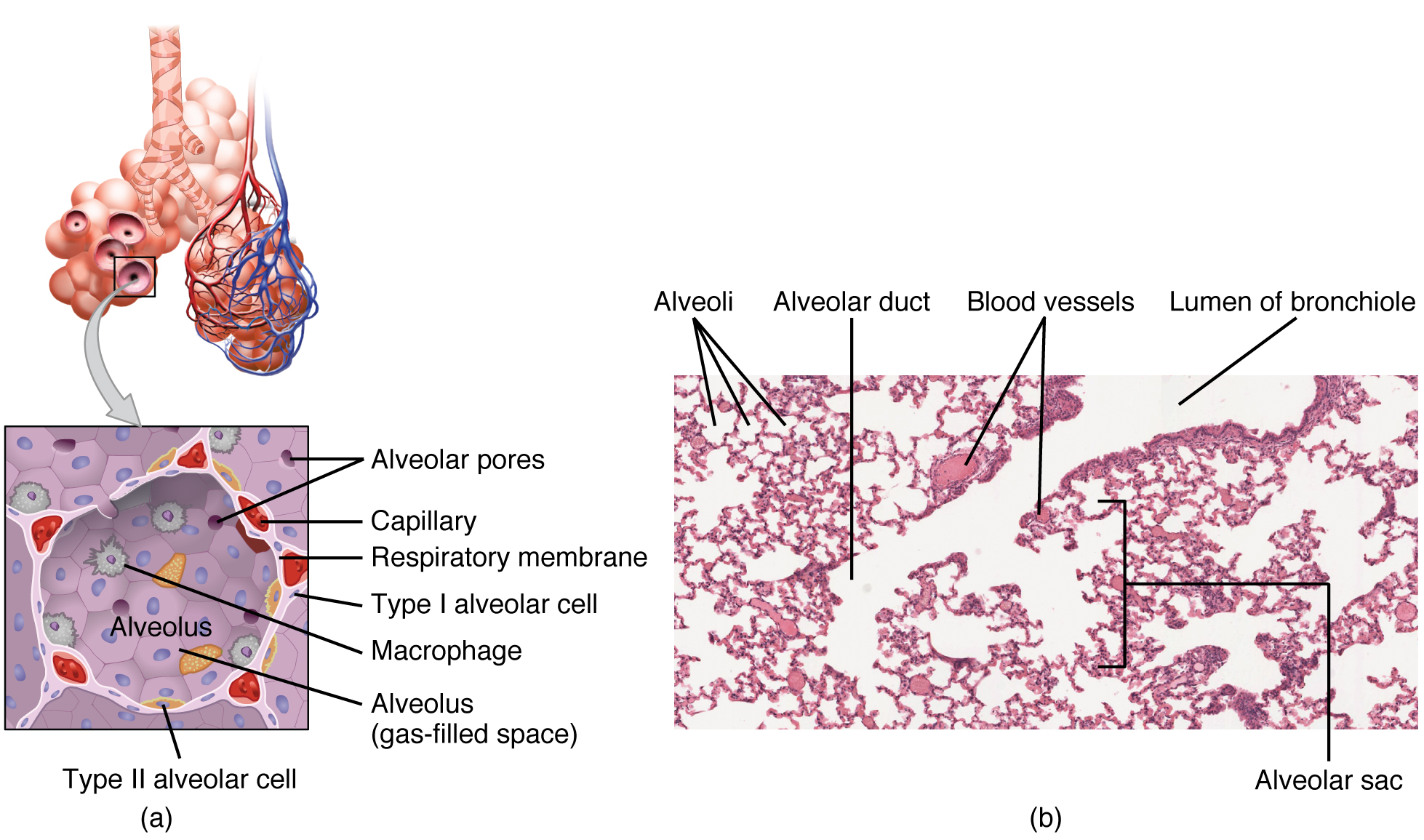
The alveolar wall consists of three major cell types: type I alveolar cells, type II alveolar cells, and alveolar macrophages. A type I alveolar cell is a squamous epithelial cell of the alveoli, which constitute up to 97 percent of the alveolar surface area. These cells are about 25 nm thick and are highly permeable to gases. A type II alveolar cell is interspersed among the type I cells and secretes pulmonary surfactant , a substance composed of phospholipids and proteins that reduces the surface tension of the alveoli. Roaming around the alveolar wall is the alveolar macrophage , a phagocytic cell of the immune system that removes debris and pathogens that have reached the alveoli.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?