| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The epiphyseal plate is the area of growth in a long bone. It is a layer of hyaline cartilage where ossification occurs in immature bones. On the epiphyseal side of the epiphyseal plate, cartilage is formed. On the diaphyseal side, cartilage is ossified, and the diaphysis grows in length. The epiphyseal plate is composed of four zones of cells and activity ( [link] ). The reserve zone is the region closest to the epiphyseal end of the plate and contains small chondrocytes within the matrix. These chondrocytes do not participate in bone growth but secure the epiphyseal plate to the osseous tissue of the epiphysis.
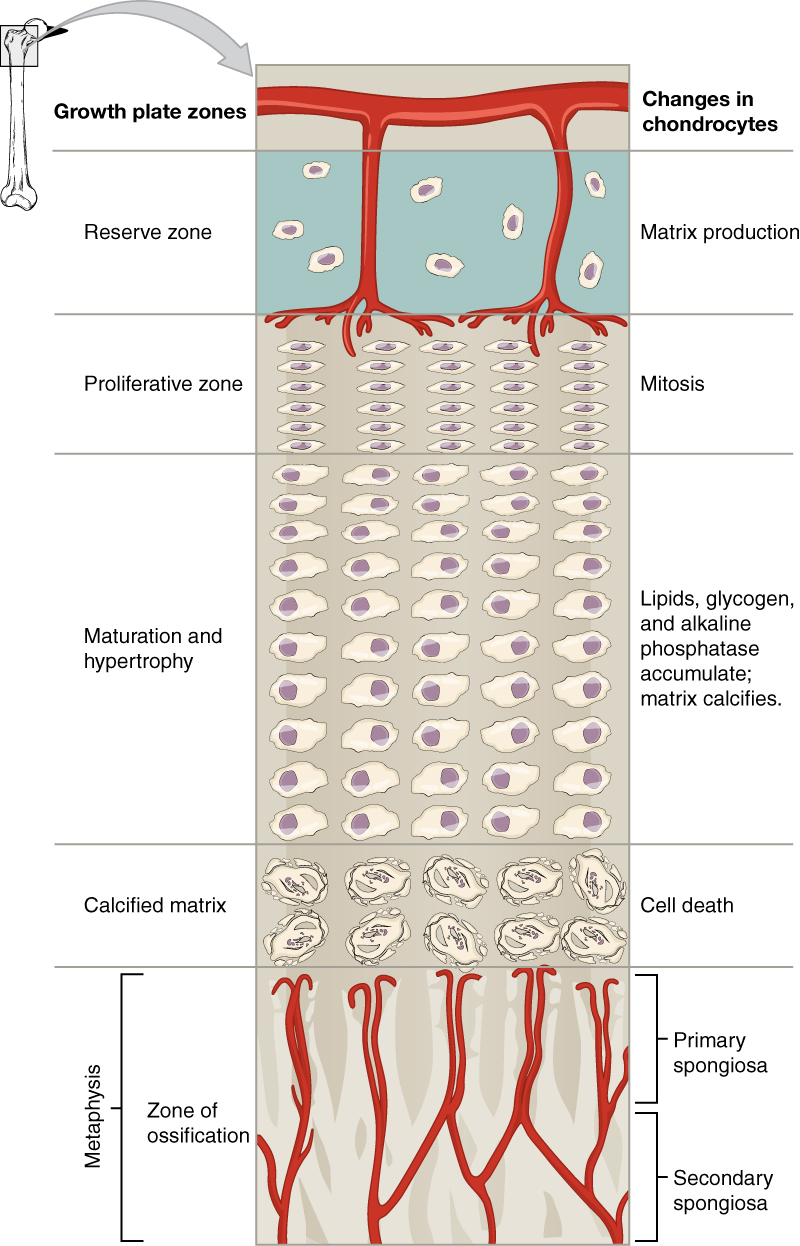
The proliferative zone is the next layer toward the diaphysis and contains stacks of slightly larger chondrocytes. It makes new chondrocytes (via mitosis) to replace those that die at the diaphyseal end of the plate. Chondrocytes in the next layer, the zone of maturation and hypertrophy , are older and larger than those in the proliferative zone. The more mature cells are situated closer to the diaphyseal end of the plate. The longitudinal growth of bone is a result of cellular division in the proliferative zone and the maturation of cells in the zone of maturation and hypertrophy.
Most of the chondrocytes in the zone of calcified matrix , the zone closest to the diaphysis, are dead because the matrix around them has calcified. Capillaries and osteoblasts from the diaphysis penetrate this zone, and the osteoblasts secrete bone tissue on the remaining calcified cartilage. Thus, the zone of calcified matrix connects the epiphyseal plate to the diaphysis. A bone grows in length when osseous tissue is added to the diaphysis.
Bones continue to grow in length until early adulthood. The rate of growth is controlled by hormones, which will be discussed later. When the chondrocytes in the epiphyseal plate cease their proliferation and bone replaces the cartilage, longitudinal growth stops. All that remains of the epiphyseal plate is the epiphyseal line ( [link] ).
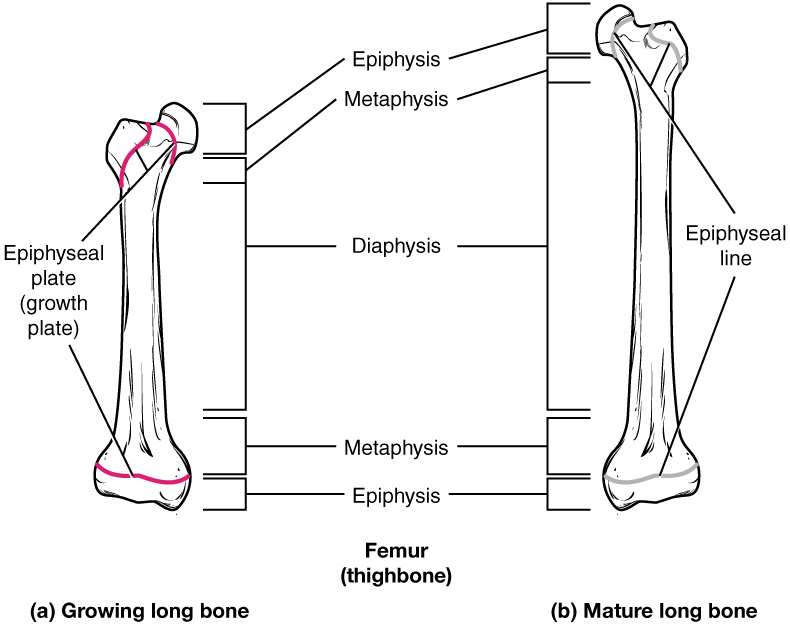
While bones are increasing in length, they are also increasing in diameter; growth in diameter can continue even after longitudinal growth ceases. This is called appositional growth. Osteoclasts resorb old bone that lines the medullary cavity, while osteoblasts, via intramembranous ossification, produce new bone tissue beneath the periosteum. The erosion of old bone along the medullary cavity and the deposition of new bone beneath the periosteum not only increase the diameter of the diaphysis but also increase the diameter of the medullary cavity. This process is called modeling .
The process in which matrix is resorbed on one surface of a bone and deposited on another is known as bone modeling. Modeling primarily takes place during a bone’s growth. However, in adult life, bone undergoes remodeling , in which resorption of old or damaged bone takes place on the same surface where osteoblasts lay new bone to replace that which is resorbed. Injury, exercise, and other activities lead to remodeling. Those influences are discussed later in the chapter, but even without injury or exercise, about 5 to 10 percent of the skeleton is remodeled annually just by destroying old bone and renewing it with fresh bone.
The genetic mutation that causes OI affects the body’s production of collagen, one of the critical components of bone matrix. The severity of the disease can range from mild to severe. Those with the most severe forms of the disease sustain many more fractures than those with a mild form. Frequent and multiple fractures typically lead to bone deformities and short stature. Bowing of the long bones and curvature of the spine are also common in people afflicted with OI. Curvature of the spine makes breathing difficult because the lungs are compressed.
Because collagen is such an important structural protein in many parts of the body, people with OI may also experience fragile skin, weak muscles, loose joints, easy bruising, frequent nosebleeds, brittle teeth, blue sclera, and hearing loss. There is no known cure for OI. Treatment focuses on helping the person retain as much independence as possible while minimizing fractures and maximizing mobility. Toward that end, safe exercises, like swimming, in which the body is less likely to experience collisions or compressive forces, are recommended. Braces to support legs, ankles, knees, and wrists are used as needed. Canes, walkers, or wheelchairs can also help compensate for weaknesses.
When bones do break, casts, splints, or wraps are used. In some cases, metal rods may be surgically implanted into the long bones of the arms and legs. Research is currently being conducted on using bisphosphonates to treat OI. Smoking and being overweight are especially risky in people with OI, since smoking is known to weaken bones, and extra body weight puts additional stress on the bones.
Watch this video to see how a bone grows.
All bone formation is a replacement process. Embryos develop a cartilaginous skeleton and various membranes. During development, these are replaced by bone during the ossification process. In intramembranous ossification, bone develops directly from sheets of mesenchymal connective tissue. In endochondral ossification, bone develops by replacing hyaline cartilage. Activity in the epiphyseal plate enables bones to grow in length. Modeling allows bones to grow in diameter. Remodeling occurs as bone is resorbed and replaced by new bone. Osteogenesis imperfecta is a genetic disease in which collagen production is altered, resulting in fragile, brittle bones.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?