| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
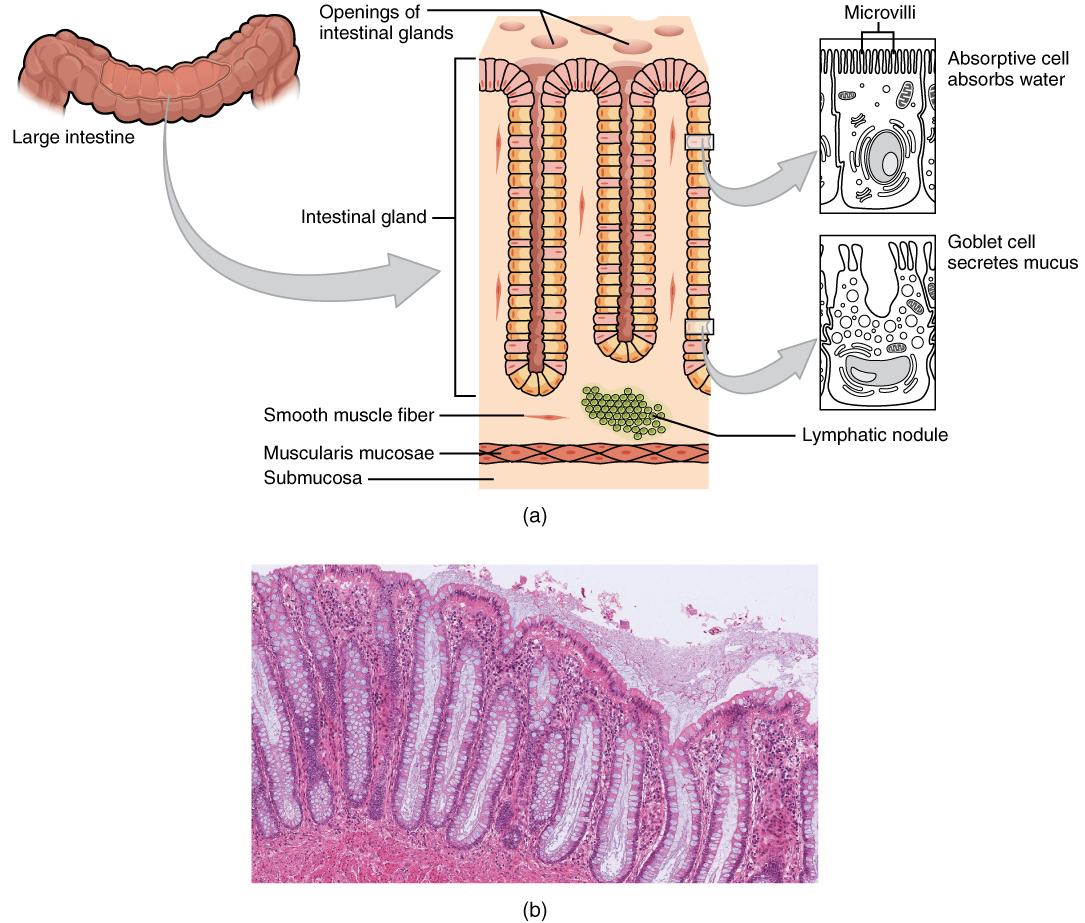
There are several notable differences between the walls of the large and small intestines ( [link] ). For example, few enzyme-secreting cells are found in the wall of the large intestine, and there are no circular folds or villi. Other than in the anal canal, the mucosa of the colon is simple columnar epithelium made mostly of enterocytes (absorptive cells) and goblet cells. In addition, the wall of the large intestine has far more intestinal glands, which contain a vast population of enterocytes and goblet cells. These goblet cells secrete mucus that eases the movement of feces and protects the intestine from the effects of the acids and gases produced by enteric bacteria. The enterocytes absorb water and salts as well as vitamins produced by your intestinal bacteria.
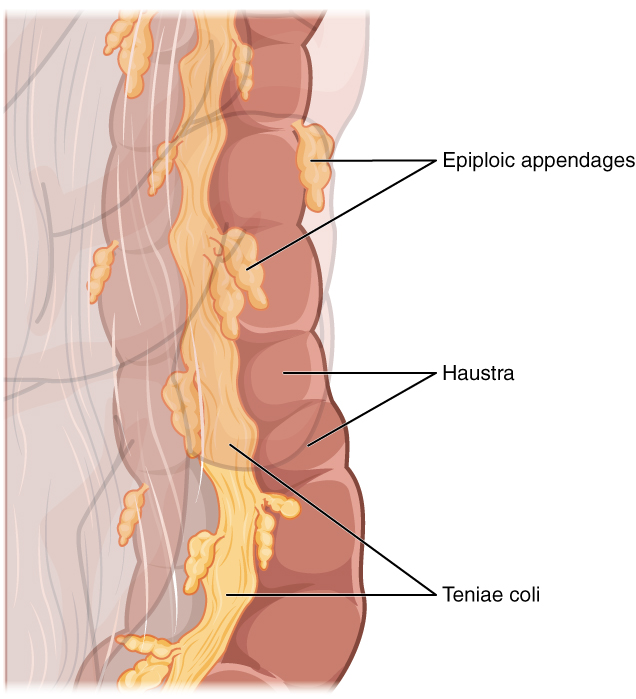
Three features are unique to the large intestine: teniae coli, haustra, and epiploic appendages ( [link] ). The teniae coli are three bands of smooth muscle that make up the longitudinal muscle layer of the muscularis of the large intestine, except at its terminal end. Tonic contractions of the teniae coli bunch up the colon into a succession of pouches called haustra (singular = hostrum), which are responsible for the wrinkled appearance of the colon. Attached to the teniae coli are small, fat-filled sacs of visceral peritoneum called epiploic appendages . The purpose of these is unknown. Although the rectum and anal canal have neither teniae coli nor haustra, they do have well-developed layers of muscularis that create the strong contractions needed for defecation.
The stratified squamous epithelial mucosa of the anal canal connects to the skin on the outside of the anus. This mucosa varies considerably from that of the rest of the colon to accommodate the high level of abrasion as feces pass through. The anal canal’s mucous membrane is organized into longitudinal folds, each called an anal column , which house a grid of arteries and veins. Two superficial venous plexuses are found in the anal canal: one within the anal columns and one at the anus.
Depressions between the anal columns, each called an anal sinus , secrete mucus that facilitates defecation. The pectinate line (or dentate line) is a horizontal, jagged band that runs circumferentially just below the level of the anal sinuses, and represents the junction between the hindgut and external skin. The mucosa above this line is fairly insensitive, whereas the area below is very sensitive. The resulting difference in pain threshold is due to the fact that the upper region is innervated by visceral sensory fibers, and the lower region is innervated by somatic sensory fibers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?