| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The term tissue is used to describe a group of cells found together in the body. The cells within a tissue share a common embryonic origin. Microscopic observation reveals that the cells in a tissue share morphological features and are arranged in an orderly pattern that achieves the tissue’s functions. From the evolutionary perspective, tissues appear in more complex organisms. For example, multicellular protists, ancient eukaryotes, do not have cells organized into tissues.
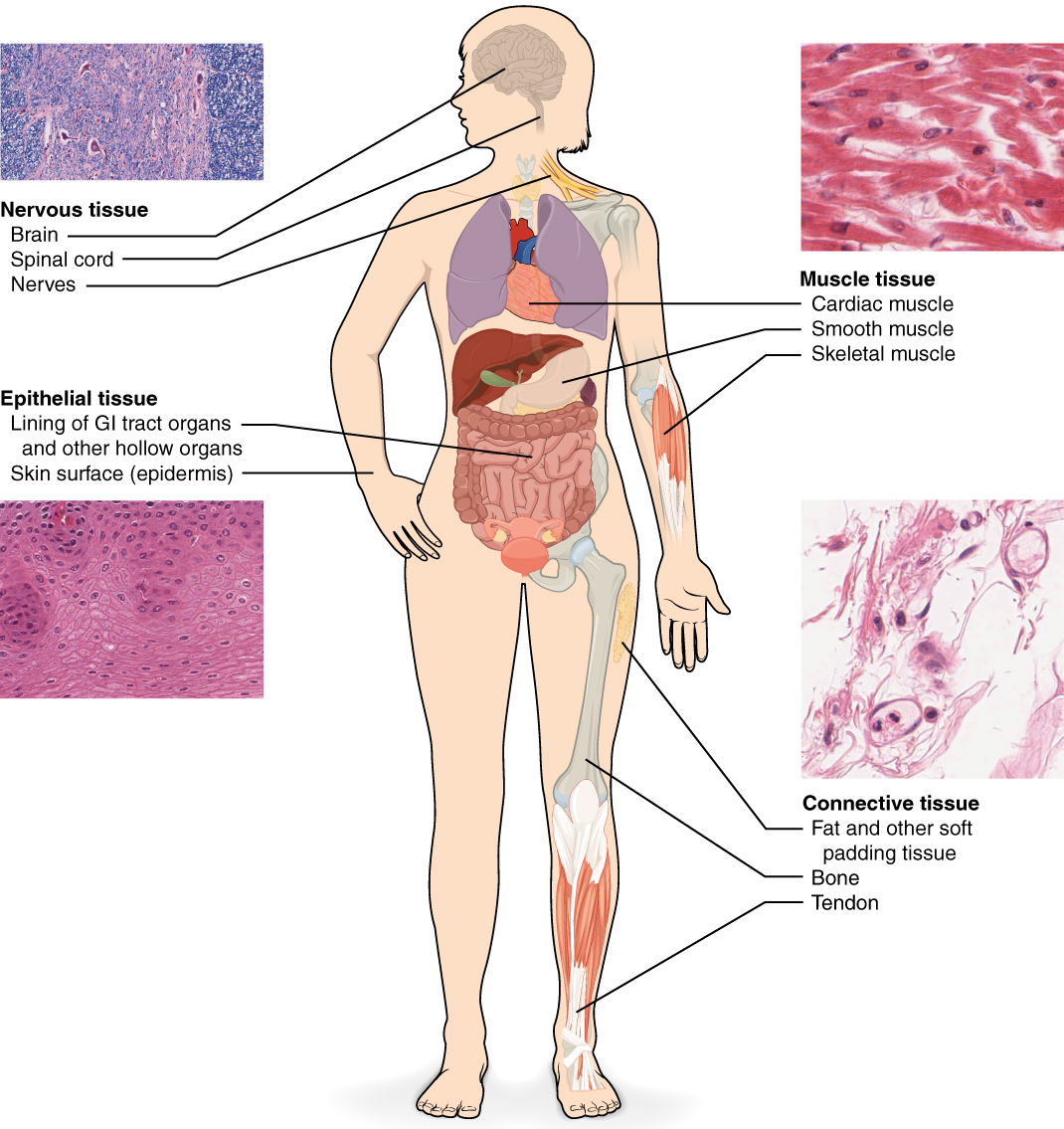
Although there are many types of cells in the human body, they are organized into four broad categories of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Each of these categories is characterized by specific functions that contribute to the overall health and maintenance of the body. A disruption of the structure is a sign of injury or disease. Such changes can be detected through histology , the microscopic study of tissue appearance, organization, and function.
Epithelial tissue , also referred to as epithelium, refers to the sheets of cells that cover exterior surfaces of the body, lines internal cavities and passageways, and forms certain glands. Connective tissue , as its name implies, binds the cells and organs of the body together and functions in the protection, support, and integration of all parts of the body. Muscle tissue is excitable, responding to stimulation and contracting to provide movement, and occurs as three major types: skeletal (voluntary) muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle in the heart. Nervous tissue is also excitable, allowing the propagation of electrochemical signals in the form of nerve impulses that communicate between different regions of the body ( [link] ).
The next level of organization is the organ, where several types of tissues come together to form a working unit. Just as knowing the structure and function of cells helps you in your study of tissues, knowledge of tissues will help you understand how organs function. The epithelial and connective tissues are discussed in detail in this chapter. Muscle and nervous tissues will be discussed only briefly in this chapter.
The zygote, or fertilized egg, is a single cell formed by the fusion of an egg and sperm. After fertilization the zygote gives rise to rapid mitotic cycles, generating many cells to form the embryo. The first embryonic cells generated have the ability to differentiate into any type of cell in the body and, as such, are called totipotent , meaning each has the capacity to divide, differentiate, and develop into a new organism. As cell proliferation progresses, three major cell lineages are established within the embryo. Each of these lineages of embryonic cells forms the distinct germ layers from which all the tissues and organs of the human body eventually form. Each germ layer is identified by its relative position: ectoderm (ecto- = “outer”), mesoderm (meso- = “middle”), and endoderm (endo- = “inner”). [link] shows the types of tissues and organs associated with the each of the three germ layers. Note that epithelial tissue originates in all three layers, whereas nervous tissue derives primarily from the ectoderm and muscle tissue from mesoderm.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?