| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Much of the body is made of protein, and these proteins take on a myriad of forms. They represent cell signaling receptors, signaling molecules, structural members, enzymes, intracellular trafficking components, extracellular matrix scaffolds, ion pumps, ion channels, oxygen and CO 2 transporters (hemoglobin). That is not even the complete list! There is protein in bones (collagen), muscles, and tendons; the hemoglobin that transports oxygen; and enzymes that catalyze all biochemical reactions. Protein is also used for growth and repair. Amid all these necessary functions, proteins also hold the potential to serve as a metabolic fuel source. Proteins are not stored for later use, so excess proteins must be converted into glucose or triglycerides, and used to supply energy or build energy reserves. Although the body can synthesize proteins from amino acids, food is an important source of those amino acids, especially because humans cannot synthesize all of the 20 amino acids used to build proteins.
The digestion of proteins begins in the stomach. When protein-rich foods enter the stomach, they are greeted by a mixture of the enzyme pepsin and hydrochloric acid (HCl; 0.5 percent). The latter produces an environmental pH of 1.5–3.5 that denatures proteins within food. Pepsin cuts proteins into smaller polypeptides and their constituent amino acids. When the food-gastric juice mixture (chyme) enters the small intestine, the pancreas releases sodium bicarbonate to neutralize the HCl. This helps to protect the lining of the intestine. The small intestine also releases digestive hormones, including secretin and CCK, which stimulate digestive processes to break down the proteins further. Secretin also stimulates the pancreas to release sodium bicarbonate. The pancreas releases most of the digestive enzymes, including the proteases trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase , which aid protein digestion. Together, all of these enzymes break complex proteins into smaller individual amino acids ( [link] ), which are then transported across the intestinal mucosa to be used to create new proteins, or to be converted into fats or acetyl CoA and used in the Krebs cycle.
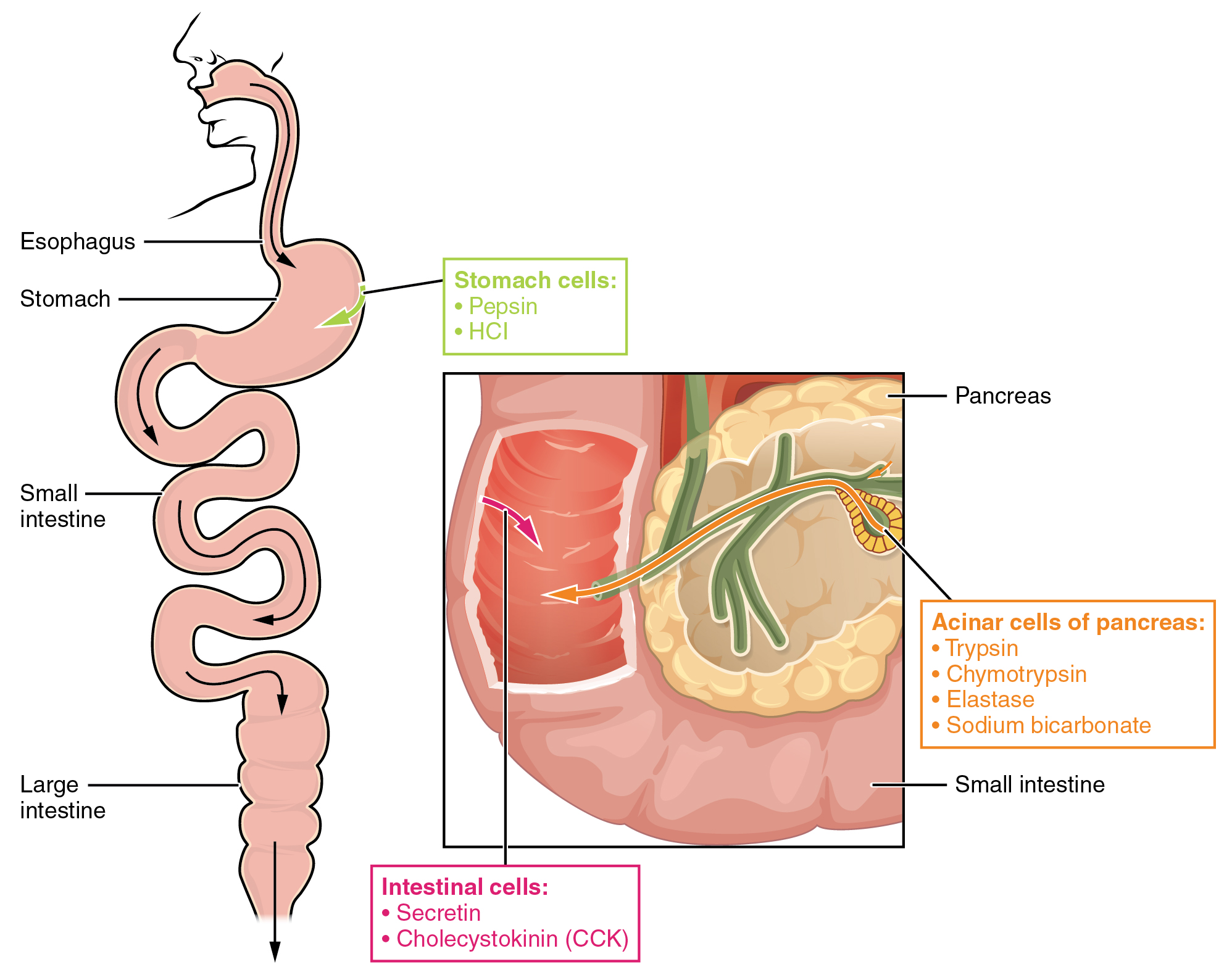
In order to avoid breaking down the proteins that make up the pancreas and small intestine, pancreatic enzymes are released as inactive proenzymes that are only activated in the small intestine. In the pancreas, vesicles store trypsin and chymotrypsin as trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen . Once released into the small intestine, an enzyme found in the wall of the small intestine, called enterokinase , binds to trypsinogen and converts it into its active form, trypsin. Trypsin then binds to chymotrypsinogen to convert it into the active chymotrypsin. Trypsin and chymotrypsin break down large proteins into smaller peptides, a process called proteolysis . These smaller peptides are catabolized into their constituent amino acids, which are transported across the apical surface of the intestinal mucosa in a process that is mediated by sodium-amino acid transporters. These transporters bind sodium and then bind the amino acid to transport it across the membrane. At the basal surface of the mucosal cells, the sodium and amino acid are released. The sodium can be reused in the transporter, whereas the amino acids are transferred into the bloodstream to be transported to the liver and cells throughout the body for protein synthesis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?