| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The family of carbohydrates includes both simple and complex sugars. Glucose and fructose are examples of simple sugars, and starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all examples of complex sugars. The complex sugars are also called polysaccharides and are made of multiple monosaccharide molecules. Polysaccharides serve as energy storage (e.g., starch and glycogen) and as structural components (e.g., chitin in insects and cellulose in plants).
During digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into simple, soluble sugars that can be transported across the intestinal wall into the circulatory system to be transported throughout the body. Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and ends with monosaccharides being absorbed across the epithelium of the small intestine. Once the absorbed monosaccharides are transported to the tissues, the process of cellular respiration begins ( [link] ). This section will focus first on glycolysis, a process where the monosaccharide glucose is oxidized, releasing the energy stored in its bonds to produce ATP.
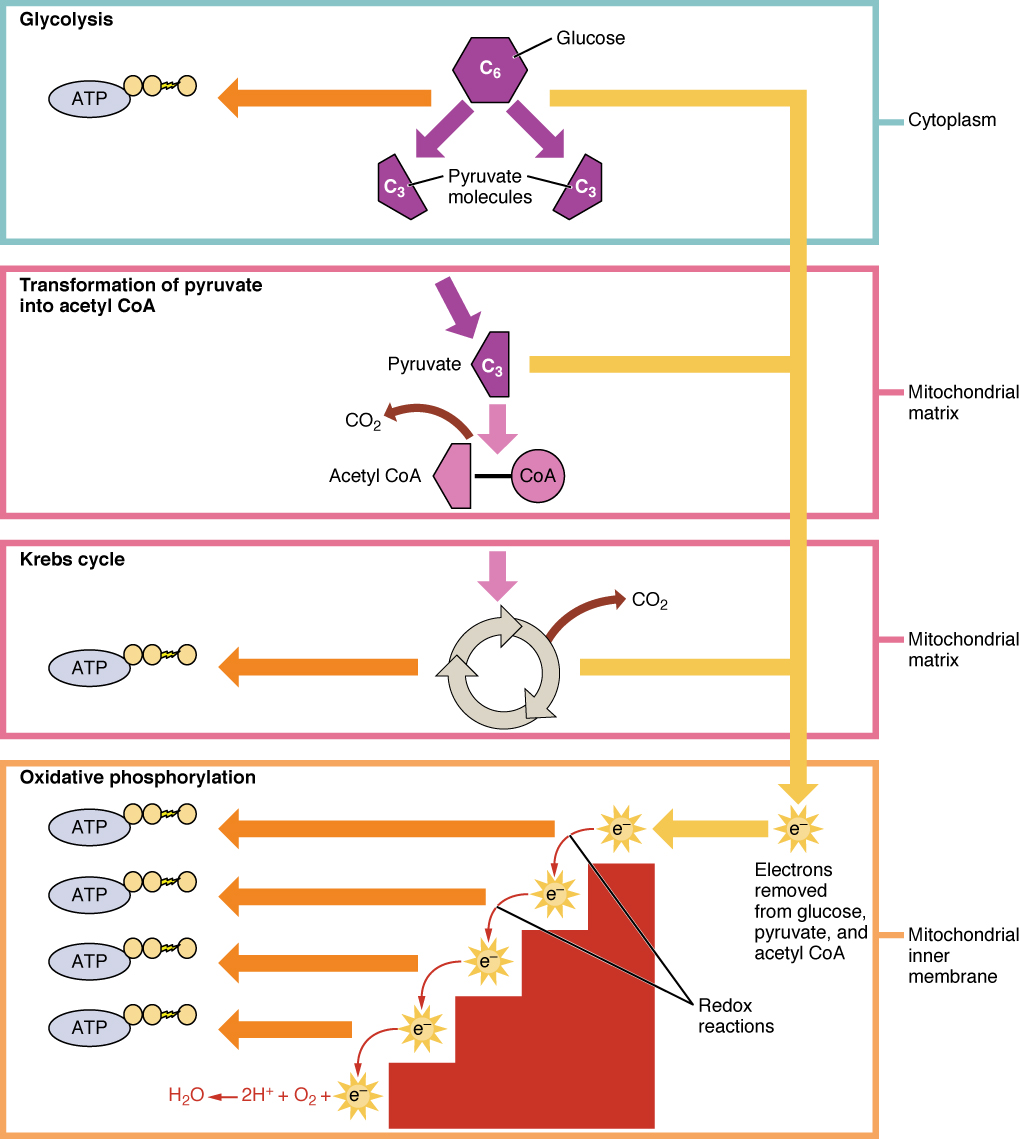
Glucose is the body’s most readily available source of energy. After digestive processes break polysaccharides down into monosaccharides, including glucose, the monosaccharides are transported across the wall of the small intestine and into the circulatory system, which transports them to the liver. In the liver, hepatocytes either pass the glucose on through the circulatory system or store excess glucose as glycogen. Cells in the body take up the circulating glucose in response to insulin and, through a series of reactions called glycolysis , transfer some of the energy in glucose to ADP to form ATP ( [link] ). The last step in glycolysis produces the product pyruvate .
Glycolysis begins with the phosphorylation of glucose by hexokinase to form glucose-6-phosphate. This step uses one ATP, which is the donor of the phosphate group. Under the action of phosphofructokinase, glucose-6-phosphate is converted into fructose-6-phosphate. At this point, a second ATP donates its phosphate group, forming fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. This six-carbon sugar is split to form two phosphorylated three-carbon molecules, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate, which are both converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is further phosphorylated with groups donated by dihydrogen phosphate present in the cell to form the three-carbon molecule 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. The energy of this reaction comes from the oxidation of (removal of electrons from) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. In a series of reactions leading to pyruvate, the two phosphate groups are then transferred to two ADPs to form two ATPs. Thus, glycolysis uses two ATPs but generates four ATPs, yielding a net gain of two ATPs and two molecules of pyruvate. In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate continues on to the Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) , where additional energy is extracted and passed on.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?