| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
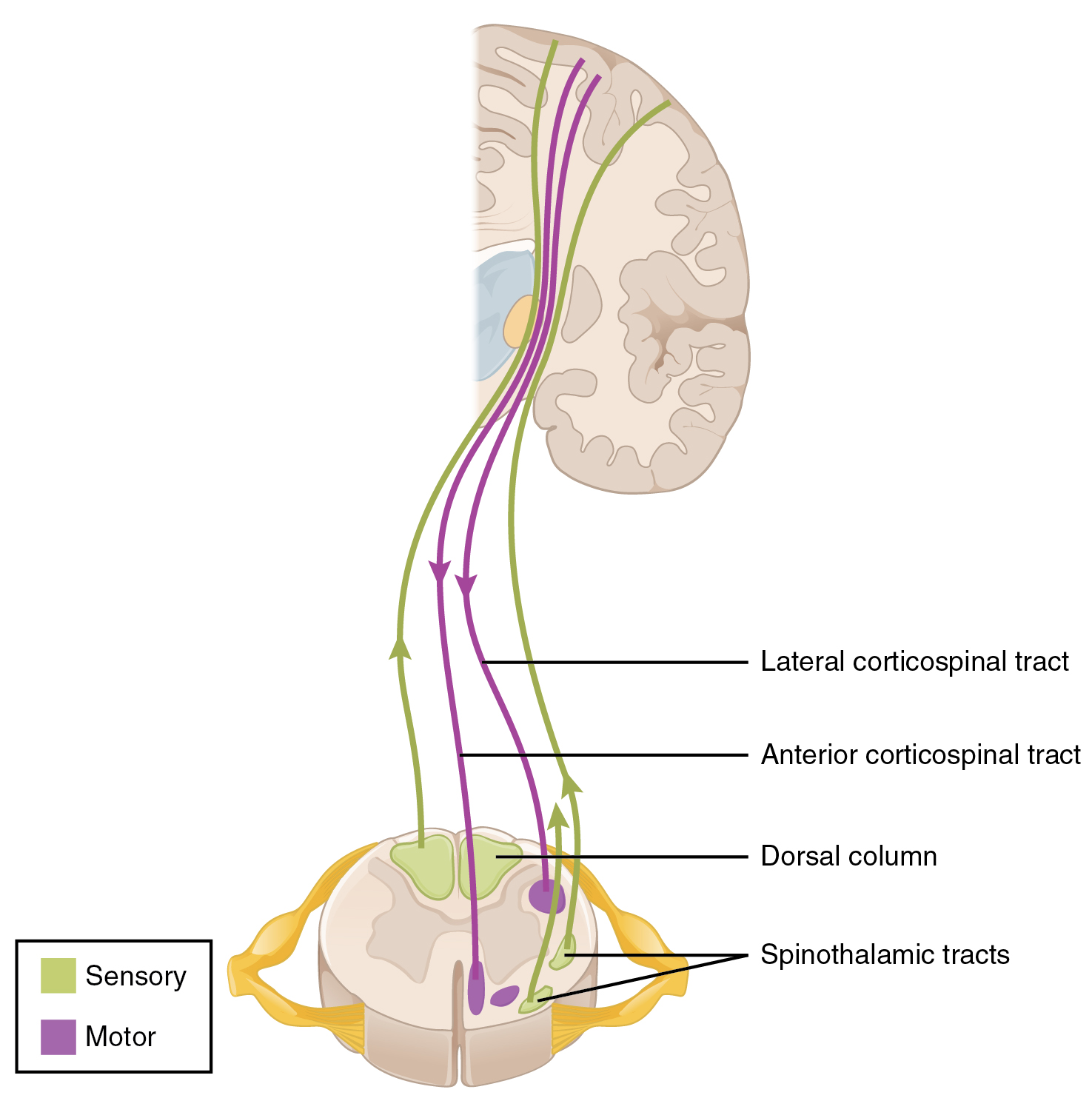
Connections between the body and the CNS occur through the spinal cord. The cranial nerves connect the head and neck directly to the brain, but the spinal cord receives sensory input and sends motor commands out to the body through the spinal nerves. Whereas the brain develops into a complex series of nuclei and fiber tracts, the spinal cord remains relatively simple in its configuration ( [link] ). From the initial neural tube early in embryonic development, the spinal cord retains a tube-like structure with gray matter surrounding the small central canal and white matter on the surface in three columns. The dorsal, or posterior, horns of the gray matter are mainly devoted to sensory functions whereas the ventral, or anterior, and lateral horns are associated with motor functions. In the white matter, the dorsal column relays sensory information to the brain, and the anterior column is almost exclusively relaying motor commands to the ventral horn motor neurons. The lateral column, however, conveys both sensory and motor information between the spinal cord and brain.
The general senses are distributed throughout the body, relying on nervous tissue incorporated into various organs. Somatic senses are incorporated mostly into the skin, muscles, or tendons, whereas the visceral senses come from nervous tissue incorporated into the majority of organs such as the heart or stomach. The somatic senses are those that usually make up the conscious perception of the how the body interacts with the environment. The visceral senses are most often below the limit of conscious perception because they are involved in homeostatic regulation through the autonomic nervous system.
The sensory exam tests the somatic senses, meaning those that are consciously perceived. Testing of the senses begins with examining the regions known as dermatomes that connect to the cortical region where somatosensation is perceived in the postcentral gyrus. To test the sensory fields, a simple stimulus of the light touch of the soft end of a cotton-tipped applicator is applied at various locations on the skin. The spinal nerves, which contain sensory fibers with dendritic endings in the skin, connect with the skin in a topographically organized manner, illustrated as dermatomes ( [link] ). For example, the fibers of eighth cervical nerve innervate the medial surface of the forearm and extend out to the fingers. In addition to testing perception at different positions on the skin, it is necessary to test sensory perception within the dermatome from distal to proximal locations in the appendages, or lateral to medial locations in the trunk. In testing the eighth cervical nerve, the patient would be asked if the touch of the cotton to the fingers or the medial forearm was perceptible, and whether there were any differences in the sensations.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?