| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The neurological exam is a clinical assessment tool used to determine what specific parts of the CNS are affected by damage or disease. It can be performed in a short time—sometimes as quickly as 5 minutes—to establish neurological function. In the emergency department, this rapid assessment can make the difference with respect to proper treatment and the extent of recovery that is possible.
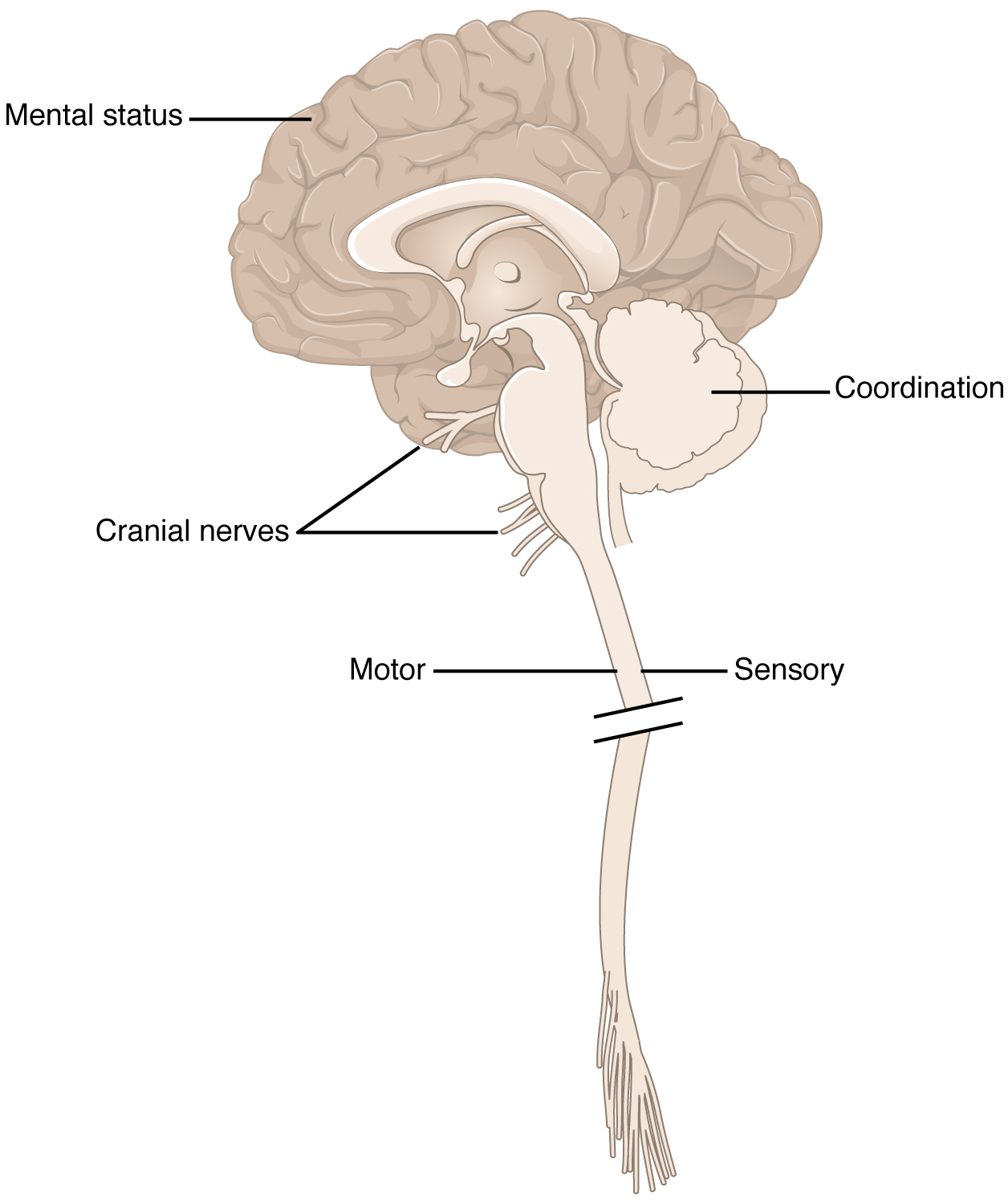
The exam is a series of subtests separated into five major sections. The first of these is the mental status exam , which assesses the higher cognitive functions such as memory, orientation, and language. Then there is the cranial nerve exam , which tests the function of the 12 cranial nerves and, therefore, the central and peripheral structures associated with them. The cranial nerve exam tests the sensory and motor functions of each of the nerves, as applicable. Two major sections, the sensory exam and the motor exam , test the sensory and motor functions associated with spinal nerves. Finally, the coordination exam tests the ability to perform complex and coordinated movements. The gait exam , which is often considered a sixth major exam, specifically assesses the motor function of walking and can be considered part of the coordination exam because walking is a coordinated movement.
Localization of function is the concept that circumscribed locations are responsible for specific functions. The neurological exam highlights this relationship. For example, the cognitive functions that are assessed in the mental status exam are based on functions in the cerebrum, mostly in the cerebral cortex. Several of the subtests examine language function. Deficits in neurological function uncovered by these examinations usually point to damage to the left cerebral cortex. In the majority of individuals, language function is localized to the left hemisphere between the superior temporal lobe and the posterior frontal lobe, including the intervening connections through the inferior parietal lobe.
The five major sections of the neurological exam are related to the major regions of the CNS ( [link] ). The mental status exam assesses functions related to the cerebrum. The cranial nerve exam is for the nerves that connect to the diencephalon and brain stem (as well as the olfactory connections to the forebrain). The coordination exam and the related gait exam primarily assess the functions of the cerebellum. The motor and sensory exams are associated with the spinal cord and its connections through the spinal nerves.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?