| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To move the skeleton, the tension created by the contraction of the fibers in most skeletal muscles is transferred to the tendons. The tendons are strong bands of dense, regular connective tissue that connect muscles to bones. The bone connection is why this muscle tissue is called skeletal muscle.
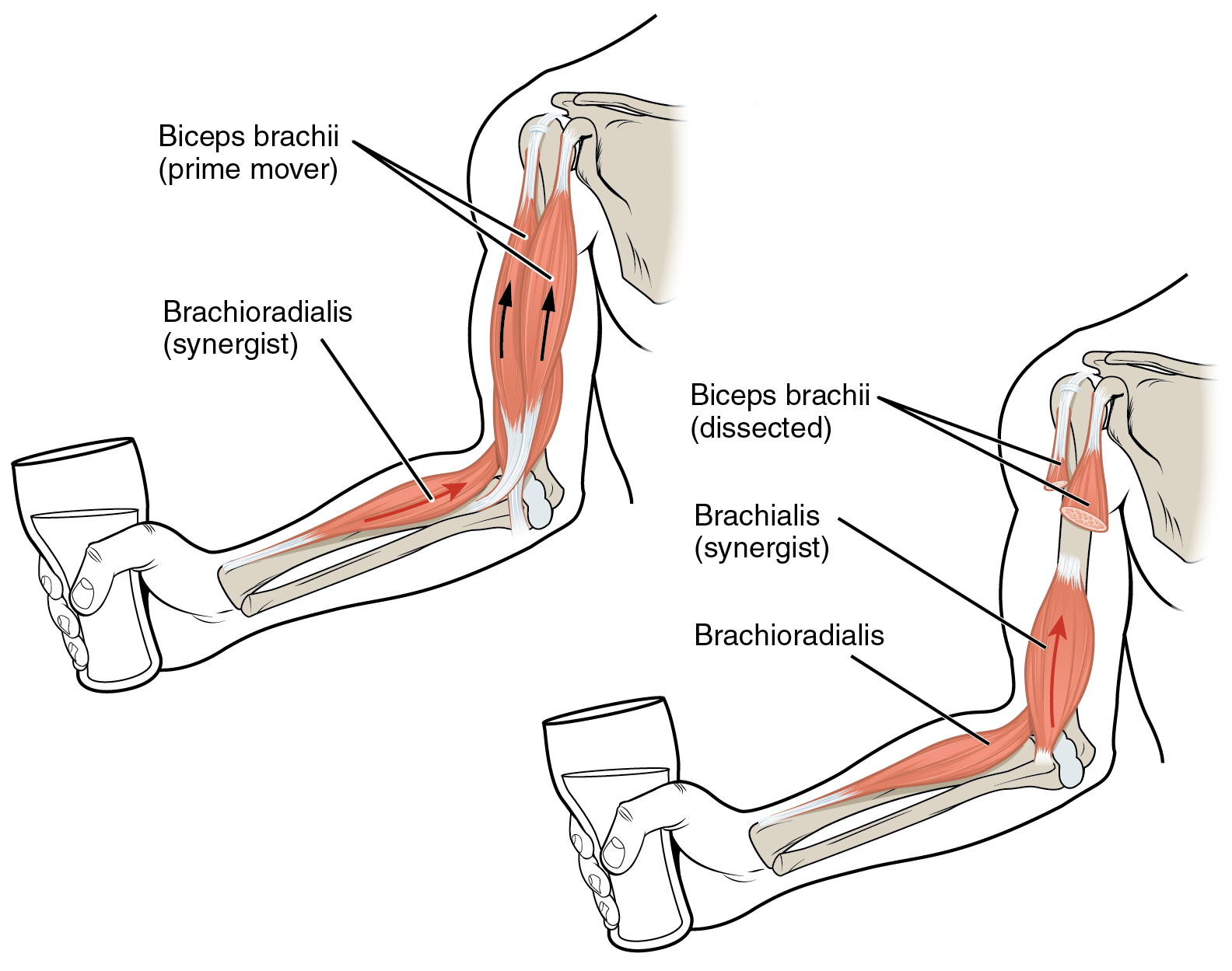
To pull on a bone, that is, to change the angle at its synovial joint, which essentially moves the skeleton, a skeletal muscle must also be attached to a fixed part of the skeleton. The moveable end of the muscle that attaches to the bone being pulled is called the muscle’s insertion , and the end of the muscle attached to a fixed (stabilized) bone is called the origin . During forearm flexion —bending the elbow—the brachioradialis assists the brachialis.
Although a number of muscles may be involved in an action, the principal muscle involved is called the prime mover , or agonist . To lift a cup, a muscle called the biceps brachii is actually the prime mover; however, because it can be assisted by the brachialis, the brachialis is called a synergist in this action ( [link] ). A synergist can also be a fixator that stabilizes the bone that is the attachment for the prime mover’s origin.
A muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist . Antagonists play two important roles in muscle function: (1) they maintain body or limb position, such as holding the arm out or standing erect; and (2) they control rapid movement, as in shadow boxing without landing a punch or the ability to check the motion of a limb.
For example, to extend the knee, a group of four muscles called the quadriceps femoris in the anterior compartment of the thigh are activated (and would be called the agonists of knee extension). However, to flex the knee joint, an opposite or antagonistic set of muscles called the hamstrings is activated.
As you can see, these terms would also be reversed for the opposing action. If you consider the first action as the knee bending, the hamstrings would be called the agonists and the quadriceps femoris would then be called the antagonists. See [link] for a list of some agonists and antagonists.
| Agonist and Antagonist Skeletal Muscle Pairs | ||
|---|---|---|
| Agonist | Antagonist | Movement |
| Biceps brachii: in the anterior compartment of the arm | Triceps brachii: in the posterior compartment of the arm | The biceps brachii flexes the forearm, whereas the triceps brachii extends it. |
| Hamstrings: group of three muscles in the posterior compartment of the thigh | Quadriceps femoris: group of four muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh | The hamstrings flex the leg, whereas the quadriceps femoris extend it. |
| Flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus: in the anterior compartment of the forearm | Extensor digitorum: in the posterior compartment of the forearm | The flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus flex the fingers and the hand at the wrist, whereas the extensor digitorum extends the fingers and the hand at the wrist. |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?