| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.
Up to now, in this chapter we have worked with squares and square roots. We will now extend our work to include higher powers and higher roots.
Let’s review some vocabulary first.
The terms ‘squared’ and ‘cubed’ come from the formulas for area of a square and volume of a cube.
It will be helpful to have a table of the powers of the integers from . See [link] .
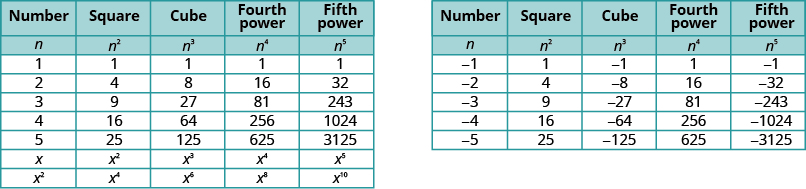
Notice the signs in [link] . All powers of positive numbers are positive, of course. But when we have a negative number, the even powers are positive and the odd powers are negative. We’ll copy the row with the powers of below to help you see this.
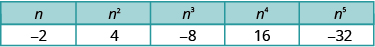
Earlier in this chapter we defined the square root of a number.
And we have used the notation to denote the principal square root . So always.
We will now extend the definition to higher roots.
If , then is an n th root of a number .
The principal n th root of is written .
n is called the index of the radical.
We do not write the index for a square root. Just like we use the word ‘cubed’ for , we use the term ‘cube root’ for .
We refer to [link] to help us find higher roots.
Could we have an even root of a negative number? No. We know that the square root of a negative number is not a real number. The same is true for any even root. Even roots of negative numbers are not real numbers. Odd roots of negative numbers are real numbers.
When is an even number and
When is an odd number, is a real number for all values of .
When we worked with square roots that had variables in the radicand, we restricted the variables to non-negative values. Now we will remove this restriction.
The odd root of a number can be either positive or negative. We have seen that .
But the even root of a non-negative number is always non-negative, because we take the principal n th root .
Suppose we start with .
How can we make sure the fourth root of −5 raised to the fourth power, is 5? We will see in the following property.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?