| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.
If you miss a problem, go back to the section listed and review the material.
After defining the terms expression and equation early in Foundations , we have used them throughout this book. We have simplified many kinds of expressions and solved many kinds of equations . We have simplified many rational expressions so far in this chapter. Now we will solve rational equations.
The definition of a rational equation is similar to the definition of equation we used in Foundations .
A rational equation is two rational expressions connected by an equal sign.
You must make sure to know the difference between rational expressions and rational equations. The equation contains an equal sign.
We have already solved linear equations that contained fractions. We found the LCD of all the fractions in the equation and then multiplied both sides of the equation by the LCD to “clear” the fractions.
Here is an example we did when we worked with linear equations:
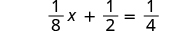 |
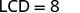 | |
| We multiplied both sides by the LCD. |
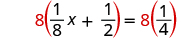 |
|
| Then we distributed. |
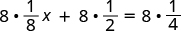 |
|
| We simplified—and then we had an equation with no fractions. |
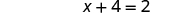 |
|
| Finally, we solved that equation. |
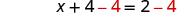 |
|
 |
We will use the same strategy to solve rational equations. We will multiply both sides of the equation by the LCD. Then we will have an equation that does not contain rational expressions and thus is much easier for us to solve.
But because the original equation may have a variable in a denominator we must be careful that we don’t end up with a solution that would make a denominator equal to zero.
So before we begin solving a rational equation, we examine it first to find the values that would make any denominators zero. That way, when we solve a rational equation we will know if there are any algebraic solutions we must discard.
An algebraic solution to a rational equation that would cause any of the rational expressions to be undefined is called an extraneous solution .
An extraneous solution to a rational equation is an algebraic solution that would cause any of the expressions in the original equation to be undefined.
We note any possible extraneous solutions, c , by writing next to the equation.
The steps of this method are shown below.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?