| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.
Until now we have dealt with solving one specific form of a linear equation. It is time now to lay out one overall strategy that can be used to solve any linear equation. Some equations we solve will not require all these steps to solve, but many will.
Beginning by simplifying each side of the equation makes the remaining steps easier.
Solve:
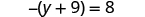 | ||
| Simplify each side of the equation as much as possible by distributing. |
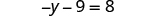 | |
| The only term is on the left side, so all variable terms are on the left side of the equation. | ||
| Add to both sides to get all constant terms on the right side of the equation. |
 | |
| Simplify. |
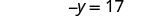 | |
| Rewrite as . |
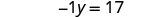 | |
| Make the coefficient of the variable term to equal to by dividing both sides by . |
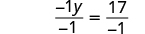 | |
| Simplify. |
 | |
| Check: |
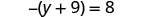 |
|
| Let . |
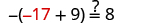 |
|
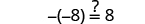 |
||
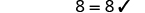 |
Solve: .
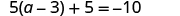 | ||
| Simplify each side of the equation as much as possible. | ||
| Distribute. |
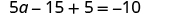 | |
| Combine like terms. |
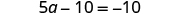 | |
| The only term is on the left side, so all variable terms are on one side of the equation. | ||
| Add to both sides to get all constant terms on the other side of the equation. |
 | |
| Simplify. |
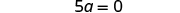 | |
| Make the coefficient of the variable term to equal to by dividing both sides by . |
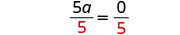 | |
| Simplify. |
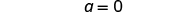 | |
| Check: |
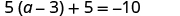 |
|
| Let . |
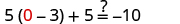 |
|
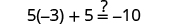 |
||
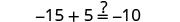 |
||
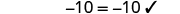 |
Solve: .
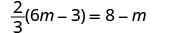 | ||
| Distribute. |
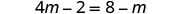 | |
| Add to get the variables only to the left. |
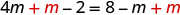 | |
| Simplify. |
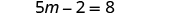 | |
| Add to get constants only on the right. |
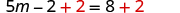 | |
| Simplify. |
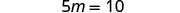 | |
| Divide by . |
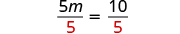 | |
| Simplify. |
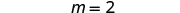 | |
| Check: |
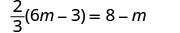 |
|
| Let . |
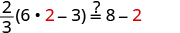 |
|
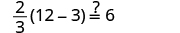 |
||
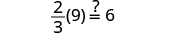 |
||
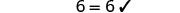 |
Solve: .
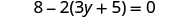 | |
| Simplify—use the Distributive Property. |
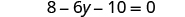 |
| Combine like terms. |
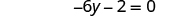 |
| Add to both sides to collect constants on the right. |
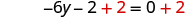 |
| Simplify. |
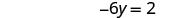 |
| Divide both sides by . |
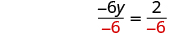 |
| Simplify. |
 |
Check: Let
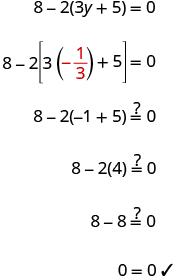 |
Solve: .
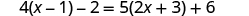 | ||
| Distribute. |
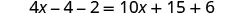 | |
| Combine like terms. |
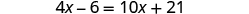 | |
| Subtract to get the variables only on the right side since . |
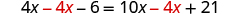 | |
| Simplify. |
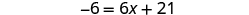 | |
| Subtract to get the constants on left. |
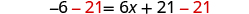 | |
| Simplify. |
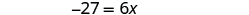 | |
| Divide by 6. |
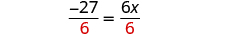 | |
| Simplify. |
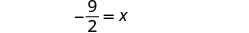 | |
| Check: |
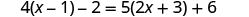 |
|
| Let . |
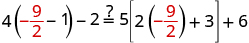 |
|
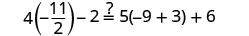 |
||
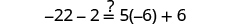 |
||
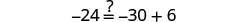 |
||
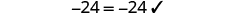 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?