| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.
In all the equations we have solved so far, all the variable terms were on only one side of the equation with the constants on the other side. This does not happen all the time—so now we will learn to solve equations in which the variable terms, or constant terms, or both are on both sides of the equation.
Our strategy will involve choosing one side of the equation to be the “variable side”, and the other side of the equation to be the “constant side.” Then, we will use the Subtraction and Addition Properties of Equality to get all the variable terms together on one side of the equation and the constant terms together on the other side.
By doing this, we will transform the equation that began with variables and constants on both sides into the form We already know how to solve equations of this form by using the Division or Multiplication Properties of Equality.
Solve:
In this equation, the variable is found only on the left side. It makes sense to call the left side the “variable” side. Therefore, the right side will be the “constant” side. We will write the labels above the equation to help us remember what goes where.
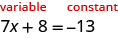
Since the left side is the “ ”, or variable side, the 8 is out of place. We must “undo” adding 8 by subtracting 8, and to keep the equality we must subtract 8 from both sides.
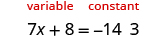 | ||
| Use the Subtraction Property of Equality. |
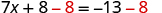 | |
| Simplify. |
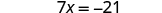 | |
| Now all the variables are on the left and the constant on the right.
The equation looks like those you learned to solve earlier. | ||
| Use the Division Property of Equality. |
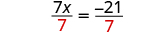 | |
| Simplify. |
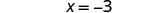 | |
| Check: |
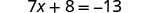 |
|
| Let . |
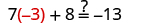 |
|
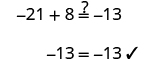 |
Solve:
Notice, the variable is only on the left side of the equation, so we will call this side the “variable” side, and the right side will be the “constant” side. Since the left side is the “variable” side, the 9 is out of place. It is subtracted from the , so to “undo” subtraction, add 9 to both sides. Remember, whatever you do to the left, you must do to the right.
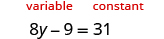 | ||
| Add 9 to both sides. |
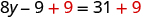 | |
| Simplify. |
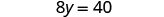 | |
| The variables are now on one side and the constants on the other.
We continue from here as we did earlier. | ||
| Divide both sides by 8. |
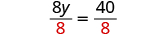 | |
| Simplify. |
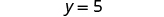 | |
| Check: |
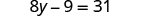 |
|
| Let . |
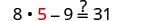 |
|
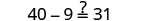 |
||
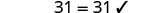 |
What if there are variables on both sides of the equation? For equations like this, begin as we did above—choose a “variable” side and a “constant” side, and then use the subtraction and addition properties of equality to collect all variables on one side and all constants on the other side.
Solve:
Here the variable is on both sides, but the constants only appear on the right side, so let’s make the right side the “constant” side. Then the left side will be the “variable” side.
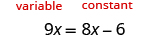 | ||
| We don’t want any ’s on the right, so subtract the from both sides. |
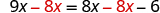 | |
| Simplify. |
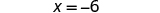 | |
| We succeeded in getting the variables on one side and the constants on the other, and have obtained the solution. | ||
| Check: |
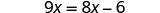 |
|
| Let . |
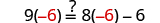 |
|
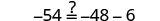 |
||
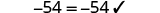 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?