| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Construct a probability model for tossing a fair coin.
| Outcome | Probability |
|---|---|
| Roll of 1 | |
| Roll of 2 | |
| Roll of 3 | |
| Roll of 4 | |
| Roll of 5 | |
| Roll of 6 |
Let be a sample space for an experiment. When investigating probability, an event is any subset of When the outcomes of an experiment are all equally likely, we can find the probability of an event by dividing the number of outcomes in the event by the total number of outcomes in Suppose a number cube is rolled, and we are interested in finding the probability of the event “rolling a number less than or equal to 4.” There are 4 possible outcomes in the event and 6 possible outcomes in so the probability of the event is
The probability of an event in an experiment with sample space with equally likely outcomes is given by
is a subset of so it is always true that
A number cube is rolled. Find the probability of rolling an odd number.
The event “rolling an odd number” contains three outcomes. There are 6 equally likely outcomes in the sample space. Divide to find the probability of the event.
A number cube is rolled. Find the probability of rolling a number greater than 2.
We are often interested in finding the probability that one of multiple events occurs. Suppose we are playing a card game, and we will win if the next card drawn is either a heart or a king. We would be interested in finding the probability of the next card being a heart or a king. The union of two events is the event that occurs if either or both events occur.
Suppose the spinner in [link] is spun. We want to find the probability of spinning orange or spinning a
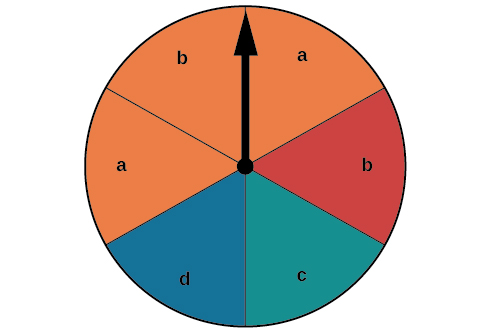
There are a total of 6 sections, and 3 of them are orange. So the probability of spinning orange is There are a total of 6 sections, and 2 of them have a So the probability of spinning a is If we added these two probabilities, we would be counting the sector that is both orange and a twice. To find the probability of spinning an orange or a we need to subtract the probability that the sector is both orange and has a
The probability of spinning orange or a is
The probability of the union of two events and (written ) equals the sum of the probability of and the probability of minus the probability of and occurring together which is called the intersection of and and is written as ).
A card is drawn from a standard deck. Find the probability of drawing a heart or a 7.
A standard deck contains an equal number of hearts, diamonds, clubs, and spades. So the probability of drawing a heart is There are four 7s in a standard deck, and there are a total of 52 cards. So the probability of drawing a 7 is
The only card in the deck that is both a heart and a 7 is the 7 of hearts, so the probability of drawing both a heart and a 7 is Substitute into the formula.
The probability of drawing a heart or a 7 is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?