| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Imagine that we are trying to find the area of a lawn so that we can determine how much grass seed to purchase. The lawn is the green portion in [link] .
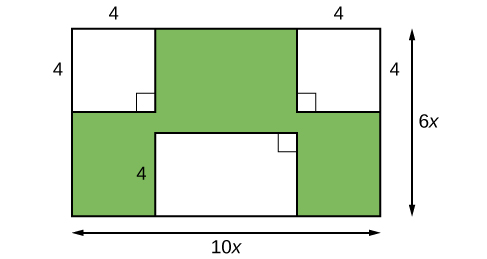
The area of the entire region can be found using the formula for the area of a rectangle.
The areas of the portions that do not require grass seed need to be subtracted from the area of the entire region. The two square regions each have an area of units 2 . The other rectangular region has one side of length and one side of length giving an area of units 2 . So the region that must be subtracted has an area of units 2 .
The area of the region that requires grass seed is found by subtracting units 2 . This area can also be expressed in factored form as units 2 . We can confirm that this is an equivalent expression by multiplying.
Many polynomial expressions can be written in simpler forms by factoring. In this section, we will look at a variety of methods that can be used to factor polynomial expressions.
When we study fractions, we learn that the greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers is the largest number that divides evenly into both numbers. For instance, is the GCF of and because it is the largest number that divides evenly into both and The GCF of polynomials works the same way: is the GCF of and because it is the largest polynomial that divides evenly into both and
When factoring a polynomial expression, our first step should be to check for a GCF. Look for the GCF of the coefficients, and then look for the GCF of the variables.
The greatest common factor (GCF) of polynomials is the largest polynomial that divides evenly into the polynomials.
Given a polynomial expression, factor out the greatest common factor.
Factor
First, find the GCF of the expression. The GCF of and is The GCF of and is (Note that the GCF of a set of expressions in the form will always be the exponent of lowest degree.) And the GCF of and is Combine these to find the GCF of the polynomial,
Next, determine what the GCF needs to be multiplied by to obtain each term of the polynomial. We find that and
Finally, write the factored expression as the product of the GCF and the sum of the terms we needed to multiply by.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra and trigonometry' conversation and receive update notifications?